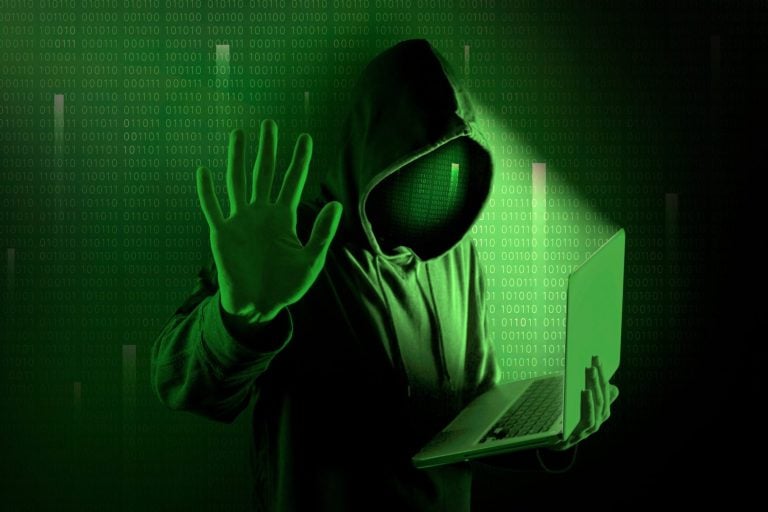
In the shadowy corners of your company’s digital infrastructure, an unseen menace lurks. It’s not ransomware or data theft – it’s cryptojacking, a silent parasite that feeds on your computing power. Right now, cybercriminals could be using your cloud resources to mine cryptocurrency, leaving you with skyrocketing energy bills and crippled performance on the victim’s computer.
Think it can’t happen to you? Think again. A staggering 86% of IT professionals reported cryptojacking incidents in their organizations last year. The worst part? Many victims don’t even know they’ve been compromised.
But here’s where it gets interesting: preventing cryptojacking isn’t just about beefing up your firewalls. It’s about understanding the psychology of these digital parasites and outsmarting them at their own game. Learning to detect cryptojacking early can mean the difference between a minor inconvenience and a full-blown crisis.
Imagine for a moment: What if you could turn the tables on these cybercriminals? What if your business could become not just secure, but impenetrable to cryptojacking attack methods?
This isn’t science fiction. It’s the new reality of cybersecurity, and it’s within your grasp. But fair warning: the solutions I’m about to share might challenge everything you think you know about protecting your business online.
Are you ready to safeguard your company’s future? To reclaim your computing power from the shadows?
Buckle up. We’re about to dive into the world of cryptojacking prevention, and trust me, it’s unlike anything you’ve seen before.

Save 80% of delivery management time
We handle everything:
- Dedicated operations manager
- Real-time tracking dashboard
- Automated customer notifications
- Urgent issue resolution
Step 1: Implementing Cryptojacking Prevention Techniques
-
Install anti-malware software and update it often.
-
Regularly check your network for strange activities.
-
Keep all software up-to-date to avoid weaknesses.
1. Use Anti-Malware Software
Anti-malware software is an essential first step in your line of defense against cryptojacking. You need to install reputable anti-malware software on every device in your business. This includes computers, servers, and mobile devices.
Installation and Configuration
Begin by selecting a reliable anti-malware software. Popular options include Norton, McAfee, and Bitdefender. Install the software on all devices. Ensure that you configure it to perform regular scans, preferably daily. These scans help detect any malicious scripts or programs that might have slipped past your defenses.
Regular Updates
Keeping your security software updated is critical. Cybercriminals frequently update their tactics. Thus, software updates can close security gaps. Set the software to update automatically. This routine updating ensures that you are protected against the latest threats. Neglecting updates can leave systems vulnerable to attacks.

2. Conduct Regular Network Audits
Network audits help you spot anomalies and potential threats. These checks should be routine to maintain a secure business and cloud environment.
Scheduling Audits
Plan network audits at least once a month. More frequent audits are even better. Each audit should involve a thorough review of your network settings. Look for unusual data flows or unauthorized access attempts.
Monthly Records
Four months within the first half of 2023 set new monthly volume records for cryptojacking attacks, with May alone recording 77.6 million hits.
Monitoring Tools
Use network monitoring tools. These tools provide real-time insights into your network’s performance. They can alert you when there is suspicious activity. Examples of these tools include SolarWinds and Nagios. Such tools can track data flow and usage patterns, helping you quickly identify and prevent cryptojacking attack and activities.
3. Update and Patch Software Regularly
Software updates and patches fix vulnerabilities that cryptojackers might exploit.
Operating Systems and Applications
Ensure all operating systems and applications are up-to-date. This includes security patches released by developers. Configure systems to apply these patches automatically when possible. Regular updates reduce the chance of cybercriminals exploiting known software flaws.
Automated Systems
Automate update processes wherever feasible. It minimizes the time and effort needed to keep software current. Some systems can check for updates and schedule installations without human intervention, ensuring continuous protection.

4. Implement Browser Security Measures
Browsers are a frequent target for cryptojackers who use malicious scripts.
Browser Extensions
Install anti-cryptojacking browser extensions like minerBlock or No Coin. These add-ons block cryptojacking scripts that can run in the background while users browse the web.
Ad Blockers and JavaScript Disabling
Use ad blockers to prevent unwanted scripts. Disable JavaScript on web browsers, to stop script-based cryptojacking. Remember, though, disabling JavaScript might affect the functionality of some websites. Adjust these settings according to your business needs.
5. Educate and Train Employees
A knowledgeable workforce is vital in preventing all types of cryptojacking.
Security Awareness Training
Conduct regular security training sessions. Educate employees about the risks and signs of cryptojacking. They should know what to look out for, such as reduced device performance and overheating.
Regular Updates on Cryptojacking Tactics
Keep everyone informed about the latest cryptojacking tactics. Share updates during employee meetings or through newsletters. Awareness reduces the risk of inadvertent mistakes leading to unauthorized access.
Cryptojacking is a growing risk, with sophisticated attacks becoming more common. Adopting the measures laid out in these steps can significantly mitigate risks to your business. Now your business is better equipped to resist these threats.
Step 2: Implementing Business Cybersecurity Measures
Install a strong firewall and keep an eye on outgoing network activities.
Train your team regularly to recognize and report cryptojacking.
Use multi-factor authentication to guard key systems.
Implementing cybersecurity measures in your business is crucial to prevent and mitigate cryptojacking threats. Let’s break down the essential steps.
1. Establish a Robust Firewall
Deploying and maintaining a solid firewall is your first line of defense. Firewalls act as barriers that monitor and filter incoming and outgoing network traffic.
Deploy Advanced Firewall Solutions
Select a firewall solution suitable for your business size and type. This could be a hardware or a software-based firewall. Set it up in a way that it allows authorized traffic and blocks anything anomalous. Ensure the firewall is compatible with your network infrastructure.
Configure Alerts for Suspicious Outbound Activities
Make sure your firewall is configured to send alerts for any unusual outbound network traffic. Setting these alerts helps quickly identify and stop potential cryptojacking attempts. Consider integrating with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems for better insight.
2. Employee Education and Training
Your employees play a crucial role in cybersecurity. Training them to identify and report cryptojacking threats is invaluable.
Conduct Regular Training Sessions
Hold scheduled sessions, perhaps quarterly, and cover various aspects of cybersecurity. Focus on real-life scenarios where cryptojacking could occur.
Geographical Spread
All regions reported increased cryptojacking incidents in recent years. North America saw a 345% rise in 2022, while Europe experienced an unprecedented 788% spike.
Educate Staff on Recognizing Cryptojacking Symptoms
Teach your team to spot sluggish systems, unexpected CPU spikes, and overheating devices. These are tell-tale signs of cryptojacking. Provide clear reporting channels for employees to report suspected issues.
3. Enforce Strong Authentication Protocols
Strengthening your authentication processes is vital in protecting your systems from unauthorized access, including cryptojacking attacks.
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring more than just a password. Use it across all your critical systems. This can include SMS codes, authentication apps, or biometrics. Implement MFA for system admins first, then extend to other vital accounts.
Regularly Update Password Policies and Guidelines
Review your password policies at least twice a year. Encourage the use of password managers to store complex, unique passwords. Set up automatic reminders for employees to change passwords every 60-90 days.
These combined cybersecurity measures will not only help prevent cryptojacking but also reinforce your business target network’s overall security posture. Keep building on these basics to provide a safe working environment and network for your business operations.
Step 3: Identifying Cryptojacking Threats
-
Spot system slowdowns linked to cryptojacking.
-
Monitor network and CPU for unusual activity.
-
Gain tools to detect browser exploitations.
1. Monitor CPU Usage Patterns
Check for Unexplained Spikes in CPU Usage
Begin by examining the central processing unit (CPU) usage on your business’s computers. Cryptojacking often causes a significant increase in CPU utilization because mining cryptocurrency demands high processing power. Regularly checking the Task Manager on Windows or the Activity Monitor on Mac will help identify unexpected spikes. A noticeable jump in CPU usage when no resource-heavy application is open can indicate a problem.
When monitoring, note the CPU usage baseline during normal operations. If there’s a 10-20% increase without explanation, investigate further.
Use System Diagnostics Tools
Implement comprehensive system diagnostic tools to dig deeper into resource consumption. Software like SolarWinds or Nagios can provide a detailed report of the CPU usage over time. These tools can help you spot trends or anomalies indicative of cryptojacking attacks. They may also alert you to consistent, unexplained resource usage, something often detailed in thorough pentesting reports for identifying hidden threats.
Regularly review tool analyses and set alerts for unusually high CPU usage to catch issues early.
2. Inspect Network Performance
Identify Slowdown in Internet Speeds
Cryptojacking scripts can affect your network by consuming bandwidth for mining operations. If your internet speeds are notably slower without any apparent cause, it could be a sign of underlying malicious activity. Monitor your internet speed regularly through service provider tools or dedicated speed test websites like Speedtest by Ookla.
Slow network performance coupled with high CPU usage often signals deeper issues related to cryptojacking.
Analyze Network Traffic
Use network monitoring software such as Wireshark to analyze traffic flows. Look for unusual traffic patterns or unauthorized connections, particularly to obscure ports or IP addresses. Cryptojacking can occur through network connections to mining pools, often involving connections to suspicious or unknown foreign IP addresses.
Pay attention to multiple connections going to the same unfamiliar IP—these are red flags.
3. Evaluate Browser Performance
Look Out for Changes in Browser Behavior
Cryptojacking scripts often run through browsers, leading to slower response times or sudden crashes. Compare browser performance when visiting common websites with and without ad blockers. Note any changes in speed or if tabs crash more frequently, as these can signal embedded mining or cryptojacking scripts embedded.
Patrick Costello from Evolve MGA highlights how system slowdowns from cryptojacking can occur, severely affecting business operations.
Use Browser Extensions to Detect Mining Scripts
Deploy browser extensions specifically designed to block mining scripts, such as No Coin or MinerBlock. These tools can prevent mining scripts from taking over your web resources. Periodically update these extensions to ensure they can block new mining scripts as they are discovered, just like regular maintenance in PC repair keeps systems protected and running smoothly.
Proactively using browser protection tools can keep your browsing experience free from cryptojacking burden.
With these steps, your business can detect and mitigate cryptojacking activities before they escalate. Keep systems under constant surveillance and remain vigilant to protect your assets.
Step 4: Protecting Corporate Networks from Cryptojacking
-
Control network access to minimize risks.
-
Filter web content to block cryptojacking scripts.
-
Use cloud tools for real-time protection.
1. Deploy Network Segmentation
Network segmentation is vital for limiting the impact of cryptojacking attacks. By aligning network components based on criticality and function, workloads are isolated, which helps in containing potential threats.
Isolate Critical Parts of Your Network
-
Define Network Zones: Split your network into different zones based on their functionalities—examples include separating internal networks, guest networks, and internet-facing systems.
-
Restrict Access with Firewalls: Use firewalls to control the flow of traffic between these zones. Make sure that only necessary data paths are open to reduce the chances of unauthorized movement within your network.
-
Monitor Traffic Between Segments: Continuous monitoring of traffic between these segments can help in detecting any anomalies or unauthorized data flows early.
Use Virtual LANs (VLANs) for Effective Segmentation
Virtual LANs (VLANs) provide logical segmentation that doesn’t rely on physical placements but can enforce similar rules.
Create VLANs: Assign VLAN IDs to different devices and network parts functioning under specific roles, ensuring separation even when they share physical infrastructure.
Enforce VLAN Policies: Use access control lists to decide what traffic can pass between VLANs. This reduces the risk of a compromised device affecting others.
Regularly Audit VLAN Configurations: Regular checks are necessary to ensure configurations align with your security policies.
2. Implement Web Content Filtering
Preventing access to sites known for cryptojacking scripts is a proactive way to protect your network.
Block Access to Malicious Websites
Use DNS Filtering: Implement DNS filtering services that block requests to domains known to host cryptojacking scripts. These services can automatically update to cover new threats as they are discovered.
Deploy Proxy Servers: Utilize proxy servers, such as residential proxies to enforce web content policies. They can block access to undesirable sites based on URLs or keywords.
Use DNS Filtering Services to Restrict Harmful Domains
Choose a Reliable DNS Service: Opt for a service with a strong reputation for updating its protective measures constantly, such as OpenDNS or Google Safe Browsing.
Integrate with Existing Systems: Make sure that the DNS filtering is integrated with your corporate security policies and tools for consistent enforcement across all devices.
3. Utilize Cloud Security Services
Cloud security services offer scalable protection that can adapt to the changing threat landscape of cryptojacking.
Leverage Cloud-Based Security Tools
Select Key Tools: Consider services like CASB (Cloud Access Security Broker) for overseeing and securing cloud applications. They monitor activity and enforce security policies in real-time.
Encryption and Key Management: Use encryption and manage keys in cloud-based solutions to safeguard data and communications.
Apply Real-Time Threat Intelligence and Response
Integrate Threat Intelligence Platforms: These platforms collect and analyze data on new threats. Use this data to adjust your security settings manually or, if possible, let the platform automate responses.
Automate Incident Responses: Adopt platforms that can automate responses to detected threats, which reduces the time your team spends on manual interventions.
Advanced Tips for Enhancing Security Measures
Endpoint detection and response leads to improved threat prevention.
Regular audits stop missed vulnerabilities.
Additional Advice or Alternative Methods
Endpoint Detection and Response Systems
Using endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems is a strategic move in advanced cybersecurity. These systems provide continuous monitoring and response to potential threats on endpoint devices. Recognized as a crucial part of modern cyber defense, EDR systems track everything from process launches to network connection attempts. In a world where threats are evolving, EDR helps not just in detection but also in understanding and responding to complex threats.
EDR systems are interesting because they work by recording detailed endpoint activity. You can collect and analyze this data to understand the scope of an attack. Businesses equipped with a solid EDR strategy are better positioned to identify and contain threats before they cause major damage. Companies are also starting to integrate EDR with other security infrastructures like security information and event management (SIEM) systems. This helps in building a more holistic approach to threat management.
Several books discuss advanced EDR systems, such as “Endpoint Detection and Response: A Comprehensive Guide” by Victor Delon. This book delves into setting up and configuring EDR systems effectively. Reading materials like these can provide deeper insights, beneficial for those looking to bolster their cybersecurity framework.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is another layer of security that detects unauthorized or malicious activities by analyzing network traffic for suspicious patterns. While EDR focuses on endpoints, IDS examines the broader network environment. This dual-layer approach creates a more comprehensive security setup.
IDS operates on predefined signatures or statistical anomaly detection methods. Signature-based IDS identifies known threats through specific patterns, while anomaly-based IDS looks for deviations from normal behavior. Each has its strengths. Signature methods are good for known threats, while anomaly systems can detect novel attacks but have a higher false positive rate.
For a more nuanced understanding of IDS, consider the book “Network Intrusion Detection: An Analyst’s Handbook” by Stephen Northcutt. This book is both practical and theoretical, offering a deep look into setting up and managing IDS environments. By complementing technical implementations with such resources, security professionals can better prepare for and respond to sophisticated attacks.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Skipping Routine Security Audits
Neglecting routine security audits is a serious mistake. Audits identify vulnerabilities that could be exploited if left unaddressed. Yet, many organizations become complacent over time, believing their current security measures are sufficient. This complacency is risky. Regular audits are critical to adapting to new threats and ensuring existing defenses are still effective.
Common barriers to regular audits include time, resources, and a lack of urgency from leadership. Yet, the average cost of a data breach has reached $4.88 million in 2024, emphasizing the financial stakes. Regularly scheduled audits, however inconvenient, are far less costly than making headlines for the wrong reason.
For further reading on conducting effective audits, “Information Security Management Principles” by David Alexander outlines practical steps and methodologies for conducting thorough security assessments. This resource can guide professionals on what to look for beyond surface-level checks.
Not Updating Security Policies
Security policies should evolve with the threat landscape. Organizations might assume that policies set a few years ago are still valid, but this assumption leaves them vulnerable. Policymakers should view updates as business-critical tasks rather than low-priority chores.
Frequent review ensures policies align with current best practices and legal requirements, such as the ever-tightening compliance regulations. Many data breaches involve human error—cited in 68% of breaches in 2024. Updated policies and training minimize mistakes like weak passwords or unintentional data exposure.
Resources like “IT Security Policies Made Easy” by Charles Cresson Wood guide readers on crafting policies that respond to evolving threats. Reading such material can help ensure that policy updates are not only timely but also effective.
Prioritizing New Security Technologies
The cybersecurity landscape is dynamic. Recent trends show an increase in AI-driven attacks, signaling the need for enhanced vigilance.
Daily Attack Expectations
A study by Netacea indicates that 93% of security leaders anticipate facing daily AI-driven attacks by the end of 2024.
Adopting new technologies like AI-driven defense mechanisms or zero-trust architectures could seem daunting. They offer proactive approaches to security, assuming no resource is trustworthy by default, thereby controlling access rigorously. Yet, even promising new tools require evaluation. Understanding the potential return on investment versus the complexity it introduces is crucial in decision-making.
Increase in Phishing Attacks:
In 2023, an average of 31,000 phishing threats were sent daily, many utilizing AI tools like ChatGPT to create convincing messages.
For expanded insights into cutting-edge technologies, “Zero Trust Networks: Building Secure Systems in Untrusted Networks” by Evan Gilman explores the practical aspects of implementing zero trust models. This subject-specific reading can offer clarity on the complex structures of next-gen security solutions.
By incorporating these advanced methods, businesses not only shield themselves more effectively from threats like cryptojacking but also construct a resilient security foundation that anticipates the future.
Conclusion
Protecting your business from cryptojacking is not just a technical challenge—it’s a strategic necessity. By implementing robust techniques to prevent cryptojacking malware, educating your team, and staying vigilant, you’ve taken crucial steps toward securing your digital assets. Remember, cybersecurity is an ongoing process. The landscape evolves, and so must your defenses. Discover strategies to shield your operations from cryptocurrency hijacking threats and ensure your company remains resilient against such cyberattacks.
As you move forward, consider each security measure as a building block in your business’s digital fortress. Regular audits, software composition analysis, and employee training on recognizing malicious code, including javascript code, are not just tasks—they’re investments in your company’s future. Take action before cryptojacking occurs. The knowledge you’ve gained is your shield against cyber threats.
Don’t let complacency creep in. Stay informed, adapt your strategies, and cultivate a security-first culture within your organization. Your proactive stance today could prevent significant losses tomorrow, especially against threats like cryptojacking, which occurs when hackers inject cryptojacking code to run cryptomining software on the victim’s computer and utilize the victim’s computing resources.
To detect cryptojacking, keep an eye out for unusual activities in your web browsers and monitor your cloud resources for any suspicious behavior. As technology advances, so do the risks—but with the insights you’ve gained, you’re well-equipped to face these challenges head-on.
Your business’s security journey doesn’t end here—it’s an ongoing commitment to protection, innovation, and resilience. Stay alert, stay secure, and keep your digital assets safe from cryptojacking threats and vulnerabilities in cloud services.


























