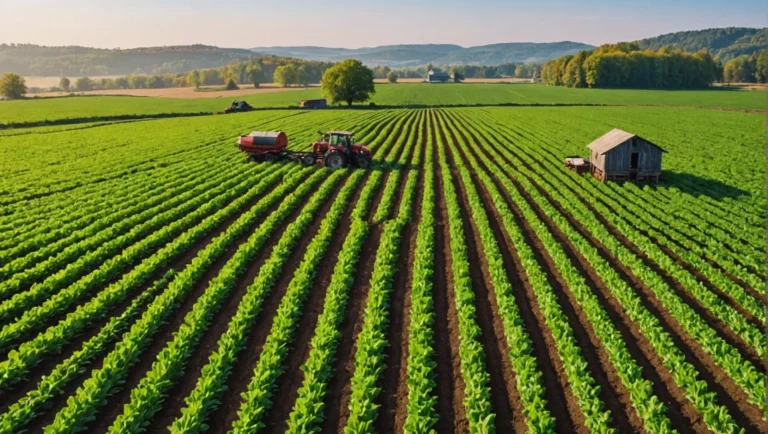
Are you tired of struggling to make ends meet on your farm? Do you feel like you’re constantly battling against rising costs and shrinking profit margins?
You’re not alone.
In today’s challenging agricultural landscape, maximizing your small farm business’s profitability is more critical than ever. But here’s the good news: there are proven strategies you can implement right now to boost your bottom line and secure your own small farm’s future.
In this article, we’ll share 10 simple strategies for a more profitable farm in 2024, including tips on maximizing crop yields and diversifying revenue streams.
Whether you’re a seasoned veteran of mushroom farming or just starting out, these practical tips will help you adapt, thrive, and build a more profitable business-resilient farming operation. Let’s dive in.

Save 80% of delivery management time
We handle everything:
- Dedicated operations manager
- Real-time tracking dashboard
- Automated customer notifications
- Urgent issue resolution
Maximize Crop Yields: Proven Profitable Small Farm Ideas
Implement Precision Agriculture Techniques
Precision agriculture is a game-changer for modern farms. By using advanced technologies like GPS mapping, soil analysis, and remote sensing, farmers can make data-driven decisions that optimize resource allocation and maximize crop yields. Embrace precision agriculture by formulating a strategic farm business plan to ensure your operation thrives through technological advancement and informed decision-making.
Utilize GPS mapping and soil analysis for targeted fertilizer application
GPS mapping allows farmers to create detailed maps of their fields, including soil type, nutrient levels, and topography. By analyzing this data, farmers can apply fertilizers precisely where they’re needed, reducing waste and improving plant growth. Soil analysis provides insights into nutrient deficiencies, pH levels, and organic matter content, enabling targeted amendments that enhance soil health and fertility.
Adopt variable rate seeding to optimize plant density and resource allocation
Variable rate seeding involves adjusting the number of seeds planted per acre based on soil conditions and yield potential. By using precision planting equipment, farmers can ensure optimal plant density in each part of the field, maximizing resource utilization and minimizing competition between plants. This technique can lead to higher yields, improved crop quality, and reduced seed costs.
Diversity Increases Profitability
Diversified farming systems have 10% higher financial profitability on average compared to simplified systems.
Employ remote sensing tools to monitor crop health and detect issues early
Remote sensing technologies, such as drones and satellite imagery, allow farmers to monitor crop health throughout the growing season. These tools can detect signs of stress, disease, or pest infestations early, enabling timely interventions that prevent yield losses. By identifying problems quickly, farmers can take targeted actions, such as spot-spraying pesticides or adjusting irrigation, to protect their crops and maintain high yields.
Invest in High-Quality Seeds and Planting Materials
Using high-quality seeds and planting materials is essential for maximizing crop yields and profitability in small farming. By selecting disease-resistant and high-yielding varieties, farmers can ensure their crops have the best chance of thriving in local conditions.
Select disease-resistant and high-yielding crop varieties
When choosing seed varieties, look for those with proven resistance to common diseases in your area. Disease-resistant crops require fewer pesticide applications, reducing input costs and minimizing the risk of yield losses. Additionally, select varieties known for their high yield potential, or high demand, as this directly impacts your farm’s profitability.
Hybrid seeds for health-conscious consumers
Hybrid seeds, created by crossing two genetically distinct parent plants, often exhibit increased vigor, uniformity, and yield potential compared to open-pollinated varieties. While hybrid seeds may have a higher upfront cost, their improved performance can lead to higher returns per acre. Evaluate the cost-benefit ratio of using hybrid seeds for your specific crops and growing conditions.
Regularly update seed stock to maintain genetic diversity and adaptability
To maintain the long-term productivity of your farm, it’s important to regularly update your seed stock. Over time, crops can become more susceptible to evolving pests and diseases, and their yield potential may decline. By introducing new varieties or rotating between different cultivars, you can maintain genetic diversity and ensure your crops remain adaptable to changing environmental conditions.
Optimize Irrigation and Water Management
Efficient water management is crucial for maximizing crop yields and reducing costs. By implementing modern irrigation systems and adopting water-saving techniques, farmers can ensure their crops receive the right amount of water while minimizing waste.
Install efficient irrigation systems like drip or sprinkler systems
Drip irrigation and sprinkler systems deliver water directly to the plant roots, reducing evaporation and runoff losses. These systems can be automated and programmed to deliver precise amounts of water based on crop requirements and weather conditions. By investing in efficient irrigation infrastructure, farmers can reduce water consumption, lower labor costs, and improve crop yields.
Implement soil moisture monitoring to avoid over or under-watering
Soil moisture sensors provide real-time data on water availability in the root zone. By monitoring soil moisture levels, farmers can make informed decisions about when and how much to irrigate. This helps prevent both over-watering, which can lead to nutrient leaching and root rot, and under-watering, which can cause drought stress and yield reductions. Soil moisture monitoring ensures crops receive optimal water levels throughout the growing season.
Adopt water-saving techniques like mulching and cover cropping
Mulching involves applying a layer of organic material, such as straw or compost, around the base of plants. This practice helps retain soil moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Cover cropping, the practice of planting non-cash crops between main crop cycles, can also improve water retention by increasing organic matter in the soil and reducing erosion. Both mulching and cover cropping contribute to more efficient water use and can help maintain high yields during periods of drought or water scarcity.
By implementing these proven strategies for maximizing crop yields, farmers can significantly boost their profitability and ensure the long-term success of their operations. Adopting precision agriculture techniques, investing in high-quality seeds, and optimizing irrigation and water management are key steps toward your traditional farming and achieving higher yields and lower costs. As you continue to refine your farming practices, stay informed about the latest innovations and best practices in the industry to maintain a competitive edge.

Metrobi is transforming farm deliveries
Specialized solutions for farm businesses:
- Farm-trained drivers
- Proper handling equipment
- Peak day delivery support
- 23% average cost reduction
Cost-Effective Farming Practices to Boost Your Bottom Line
Maximizing crop yields is essential for increasing farm profitability, but it’s equally important to focus on cost-effective farming practices that can boost your bottom line. By optimizing your farm’s size, implementing efficient machinery management, and adopting sustainable farming methods, you can reduce expenses and increase your overall profitability.
Right-Size Your Farm Operation
Assessing your land, labor, and capital resources is crucial in determining the optimal size for your farm operation. By focusing on high-value crops and livestock that align with your small-scale farm, you can maximize your profitability without overextending your resources.
Evaluating Land, Labor, and Capital
Before making any significant changes to your farm size, conduct a thorough evaluation of your available land, labor, and capital. Consider factors such as soil quality, water availability, and market demand for specific crops or livestock. This assessment will help you determine the most suitable crops and livestock for your farm that’s unique characteristics.
Focusing on High-Value Crops and Livestock
Once you have assessed your resources, identify high-value crops and livestock that align with your farm’s scale and market demand. Research current market trends, consumer preferences, local markets, and regional opportunities to make informed decisions. By concentrating on high-value products and niche markets, you can optimize your profitability without overextending your resources.
Gradual Expansion Based on Profitability
As your farm becomes more profitable and market demand allows, consider gradually expanding your operation. This approach helps minimize risk and ensures that you have the necessary resources to support growth. Continuously monitor your farm’s financial performance and make data-driven decisions when considering expansion opportunities.
Implement Efficient Machinery Management for a Higher Profitable Farm
Investing in versatile, multi-purpose equipment can significantly reduce overhead costs associated with purchasing and maintaining multiple machines. By establishing a regular maintenance schedule and exploring leasing or sharing options, you can further optimize your machinery management and reduce expenses.
Investing in Multi-Purpose Equipment
When purchasing new machinery, opt for versatile, multi-purpose equipment that can perform multiple tasks. This approach reduces the need for multiple specialized machines, lowering initial investment costs and ongoing maintenance expenses. Research the latest innovations in agricultural machinery to identify equipment that can streamline your operations and increase efficiency.
Establishing a Regular Maintenance Schedule
Implementing a regular maintenance schedule for your machinery is essential for extending its lifespan and minimizing repair costs. Train your staff to perform routine maintenance tasks and keep detailed records of each machine’s service history. By proactively maintaining your equipment, you can reduce downtime and ensure that your machinery is always operating at peak performance.
Exploring Leasing and Sharing Options
In some cases, leasing equipment or sharing machinery with neighboring farms can be a cost-effective alternative to purchasing new equipment outright. Evaluate your machinery needs and explore leasing options that align with your budget and operational requirements. Additionally, consider collaborating with nearby farms to share equipment, splitting the costs, and maximizing the use of each machine.
Adopt Sustainable Farming Methods
Sustainable farming practices not only benefit the environment but can also help reduce input costs and improve your farm’s long-term profitability. By implementing crop rotation, integrating cover cropping, and exploring reduced tillage or no-till practices, you can enhance soil health, suppress weeds, and minimize fuel and labor expenses.
Sustainable and Organic Practices
About 30% of U.S. farms are reported to be using sustainable or organic farming practices.
Implementing Crop Rotation
Crop rotation involves planting different crops in the same field over multiple growing seasons. This practice helps improve soil health by reducing nutrient depletion, minimizing pest and disease pressure, and enhancing soil structure. By implementing a well-planned crop rotation system, you can reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, lowering your input costs.
Integrating Cover Cropping
Cover cropping is the practice of planting crops primarily to improve soil health rather than for harvest. Cover crops can suppress weeds, reduce soil erosion, and enhance nutrient cycling. By integrating cover crops into your farming system, you can minimize the need for herbicides and fertilizers, reducing your overall input costs.
Exploring Reduced Tillage or No-Till Practices
Reduced tillage and no-till practices minimize soil disturbance, helping to conserve soil moisture, reduce erosion, and improve soil structure. These practices can also lower fuel and labor expenses associated with traditional tillage methods. While transitioning to reduced tillage or no-till may require an initial investment in specialized equipment, the long-term benefits can significantly improve your farm’s profitability.
Regarding farm size and profitability, the optimal size varies depending on factors such as location, crop type, and market conditions. While larger farms can benefit from economies of scale, smaller farms can be profitable by focusing on high-value crops, direct marketing, specialty markets, and value-added products. A 5-acre farm can be profitable if it specializes in niche products or serves a local market, while a larger farm may be necessary for commodity crops or to achieve self-sufficiency in poultry farming.
By implementing cost-effective farming practices, such as right-sizing your operation, managing machinery efficiently, and adopting sustainable methods, you can significantly boost your farm’s bottom line. As you continue to optimize your farm’s profitability, consider diversifying your revenue streams to ensure long-term stability and success.
Diversify Your Farm Revenue Streams for Long-Term Stability
Explore Value-Added Products and Services
Process Raw Farm Products
One effective way to increase your farm’s profitability is by processing your raw farm products into higher-value goods. This approach allows you to capture a larger share of the value chain and command higher prices for your products. For example, if you grow fruits, consider turning them into jams, jellies, or preserves. If you raise dairy animals, explore cheese-making or yogurt production. Wool from sheep can be spun into yarn or woven into fabric. By adding value to your raw products, you open up new markets and revenue streams to sell farm products.
Offer Agritourism Experiences
Another avenue for diversifying your farm income is through agritourism. By offering farm tours, workshops, or hands-on experiences, you can attract visitors and generate additional revenue. Consider setting up a farm stand or a community-supported agriculture (CSA) program to sell your products directly to consumers. This direct-to-consumer approach allows you to build relationships with your customers and capture a higher percentage of the retail price. Ensure compliance with local regulations and insurance requirements for agritourism activities to protect your farm.
Consider Agroforestry and Silvopasture Systems
Integrate Trees with Crops or Livestock
Agroforestry and silvopasture systems involve integrating trees with crops or livestock on the same land. This approach can diversify your yields and provide multiple income streams. Trees can provide timber, firewood, or specialty wood products for supplemental revenue. Additionally, tree crops like fruit, nuts, or maple syrup can offer additional income opportunities. By strategically incorporating trees into your farming system, you can enhance biodiversity, improve soil health, and create a more resilient and profitable farm. Consult with local extension services or agroforestry experts to determine the most suitable tree species and integration strategies for your specific farm conditions and goals.
Benefits of Agroforestry and Silvopasture
Agroforestry and silvopasture systems offer numerous benefits beyond diversified income streams. Trees can provide shade and shelter for livestock, reducing heat stress and improving animal welfare. They can also act as windbreaks, reducing soil erosion and protecting crops. The deep roots of trees help to improve soil structure, increase water infiltration, and enhance nutrient cycling. By creating a more diverse and resilient ecosystem, agroforestry and silvopasture can contribute to the long-term sustainability and profitability of your farm.
Gross Contribution
Farming accounts for approximately 1% of the U.S. gross domestic product.
Create a Comprehensive Agricultural Financial Plan
Develop a Detailed Budget and Cash Flow Projection
Creating a comprehensive budget is the foundation of your agricultural financial plan. Start by listing all your farm’s income sources, such as crop sales, livestock sales, and any additional revenue streams you’ve established through diversification efforts. Next, account for all operating expenses, including seeds, fertilizers, pest control, equipment maintenance, labor costs, and overhead expenses like utilities and insurance premiums. Establish a robust bookkeeping routine for your farm to ensure every financial detail is meticulously recorded and easily accessible.
Once you have a clear picture of your income and expenses, project your cash inflows and outflows for the upcoming year. This will help you identify potential shortfalls and plan accordingly. Consider using a spreadsheet or specialized farm accounting software to streamline the process and ensure accuracy.
An Average Farm's Feeding Power
One U.S. farm can feed an average of 166 people annually, both domestically and internationally.
Regularly Review and Adjust Your Budget
Your budget is a living document that should be reviewed and adjusted regularly based on actual performance. Set aside time each month to compare your projected figures with your actual income and expenses. This will help you identify areas where you may need to cut costs or explore additional revenue opportunities.
Secure Appropriate Financing and Insurance Coverage
Ensuring your farm has access to sufficient capital is crucial for maintaining operations and investing in growth opportunities. Research government grants and low-interest loans designed specifically for agricultural businesses. These programs can provide valuable financial support, particularly during challenging times, growing markets, or when you’re looking to expand your operations.
In addition to securing financing, it’s essential to maintain adequate insurance coverage to protect your farm against potential losses. Crop insurance can safeguard your income in the event of yield or price losses due to weather events, pests, or market fluctuations. Business interruption insurance can provide a safety net if your farm is forced to suspend operations due to unexpected events like natural disasters or equipment failures.
Work with a Trusted Financial Advisor
Navigating the complex world of agricultural finance can be overwhelming, especially when you’re focused on the day-to-day operations of your farm. Consider partnering with a trusted financial advisor who specializes in working with agricultural businesses. They can help you develop a comprehensive financial plan, identify appropriate financing options, and ensure you have the right insurance coverage in place.
By developing a detailed budget, securing appropriate financing, and maintaining adequate insurance coverage, you’ll create a solid foundation for your farm’s long-term financial success. Regularly reviewing and updating your financial plan will help you stay on track and adapt to changing circumstances, ensuring your farm remains profitable for years to come. Craft a farm business strategy that outlines your vision and steps for achieving profitability to guide your agricultural venture toward sustainable success.
What is Farm Profitability?
Farm profitability is the ability of a farm to generate revenue exceeding its operating costs
Factors like production efficiency, market prices, input costs, and government policies affect farm profitability
Measuring and improving farm profitability is crucial for long-term sustainability and growth in urban agriculture. agriculture
Definition of Farm Profitability
Farm profitability refers to the financial performance of an agricultural operation, specifically its capacity to generate revenue that surpasses its operating expenses. It is typically measured by calculating the net farm income, which is the difference between the total revenue earned from the sale of crops, livestock, and other farm products, and the total expenses incurred in the production process.
Profitability is a key indicator of a farm’s financial health and long-term sustainability. A profitable farm can reinvest in its operations, expand its production, and weather economic downturns more effectively than a farm operating at a loss.
Key Factors Affecting Farm Profitability
Several factors can significantly impact a farm’s profitability, including:
Production Efficiency and Yields
The efficiency with which a farm converts inputs (such as seed, fertilizer, and labor) into outputs (like crops and livestock) is a critical determinant of its profitability. Higher yields per acre or per animal can lead to increased revenue, while poor yields can result in financial losses.
Farmers can improve production efficiency by adopting best management practices, such as precision agriculture techniques, optimized irrigation systems, and integrated pest management. Investing in modern technology and equipment can also help boost efficiency and yields.
Tech Drives Farm Efficiency
Technologies can cut costs by up to 25% while increasing yields by 5%.
Market Prices for Farm Products
The prices that farmers receive for their products can have a significant impact on their profitability. Commodity prices are often volatile and subject to global market forces, making it challenging for farmers to predict and plan for future income.
Diversifying the farm’s product mix and exploring value-added products beyond profitable crops can help mitigate the risk of price fluctuations. Some farmers also use forward contracts, futures markets, or other risk management tools to lock in prices and reduce uncertainty. The National Agricultural Statistics Service reports that the average price of corn in the United States was $4.20 per bushel in 2022.
Input Costs
The costs of inputs such as seed, fertilizer, fuel, and labor can eat into a farm’s profitability if not carefully managed. Rising input costs can squeeze profit margins, especially if market prices for farm products do not keep pace.
Farmers can control input costs by implementing efficient practices, negotiating better prices with suppliers, and exploring alternative inputs or production methods. For example, using cover crops and crop rotation can reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. The Farm Financial Standards Council recommends that farmers aim to keep input costs below 70% of their total revenue.
Government Policies and Support Programs
Agricultural policies and government support programs can have a significant impact on farm profitability. Subsidies, crop insurance, and other risk management tools can help stabilize farm income and mitigate the impact of market volatility or weather-related losses.
However, changes in government policies or funding levels can also create uncertainty and financial challenges for farmers. Staying informed about agricultural policy developments and actively participating in industry organizations can help farmers navigate this complex landscape. The USDA provides information on various support programs and policies on its website.
Weather and Environmental Conditions
Weather and environmental factors, such as drought, flooding, pests, and disease, can have a dramatic impact on farm profitability. Crop failures or livestock losses due to adverse weather events can wipe out a farm’s income for an entire season.
Investing in irrigation systems, drainage improvements, and other infrastructure can help mitigate the impact of weather-related risks. Farmers can also use tools like crop insurance and diversification to spread risk and protect against catastrophic losses. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) provides data on weather patterns and climate trends that can help farmers plan for weather-related risks.
Why is Farming Profitability a Challenge?
Market Volatility and Price Fluctuations
Farming profitability is heavily influenced by the prices farmers receive for their products. These prices are determined by global supply and demand factors, which can be highly volatile. For example, a bumper crop in a major producing country can lead to oversupply and lower prices, while a drought or pest outbreak can reduce supply and drive prices up.
Farmers have limited control over the prices they receive, as they are typically price takers rather than price setters. This means they must accept the prevailing market price for their products, regardless of their production costs. Price volatility can make it difficult for farmers to plan and invest in their operations, as they cannot be certain of their future income.
According to the USDA Economic Research Service, agricultural commodity prices have been subject to significant fluctuations in recent years, with the FAO Food Price Index indicating a 15% increase in global food prices between 2020 and 2022.
Rising Input Costs and Narrowing Profit Margins
While farmers have limited control over the prices they receive, they also face rising costs for essential inputs like fuel, fertilizer, and seed. These costs have been increasing faster than farm product prices, putting pressure on farmers’ markets for premium prices and on profit margins.
Fuel and Energy Costs
Fuel and energy costs are a significant expense for farmers, as they are needed to power tractors, irrigation systems, and other equipment. As oil prices rise, so do the costs of running a farm. According to the USDA, fuel and oil costs for U.S. farms increased by 42% between 2020 and 2021.
Fertilizer and Chemical Costs
Fertilizers and agricultural chemicals are another major input cost for farmers. These products are essential for maintaining soil fertility and controlling pests and diseases. However, the prices of these inputs have been rising due to increased demand, supply chain disruptions, and higher production costs. In 2021, U.S. farmers spent 17% more on fertilizer and lime than in the previous year.
Climate Change and Weather Variability
Climate change is making weather patterns more unpredictable and extreme, posing significant challenges for farmers. Droughts, floods, heat waves, and cold snaps can all reduce crop yields and quality, leading to lower profitability.
Drought and Water Scarcity
As temperatures rise and rainfall patterns change, many farming regions are experiencing more frequent and severe droughts. This can lead to crop failures and reduced yields, as well as increased costs for irrigation. In California, for example, the 2012-2016 drought cost the state’s agricultural sector an estimated $3.8 billion.
Extreme Weather Events
Climate change is also increasing the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events like hurricanes, tornadoes, and hailstorms. These events can damage crops, destroy infrastructure, and disrupt supply chains, all of which can impact farm profitability. In 2020, extreme weather events caused an estimated $22 billion in losses for the U.S. agricultural sector.
To adapt to these challenges, farmers need to invest in resilient infrastructure, water-efficient technologies, and climate-smart farming practices. However, these investments can be costly and may not pay off immediately, further squeezing profit margins in the short term.
Boosting Your Farm’s Profitability: A Roadmap to Success
Maximizing crop yields, implementing cost-effective practices, diversifying revenue streams, and creating a comprehensive financial plan are key strategies to increase your farm’s profitability in 2024. By focusing on these areas, you can optimize your resources, reduce expenses, and create a more resilient and profitable farming operation.
The value of these strategies lies in their ability to help you adapt to changing market conditions, weather variability, and other challenges facing modern agriculture. By taking proactive steps to boost efficiency, diversify your income, and plan for the future, you can build a more sustainable and profitable farm business.
To get started, assess your current farm operation and identify areas for improvement. Prioritize the strategies that align the most profitable crops with your goals and resources, and develop a step-by-step implementation plan. Consider seeking guidance from agricultural experts, financial advisors own businesses, or experienced farmers to help you navigate this process.
What one action can you take today to move your small farms or farm towards sustainable agriculture and increased profitability?